11/06 DFS & BFS
DFS
아래의 그림과 같은 그래프가 있을 때 1번 노드를 시작으로 깊이 우선 탐색을 했을 때의 경로를 구하라. 단 인접한 노드 중 방문하지 않은 노드가 여러개 있으면 번호가 낮은 순서부터 방문한다.
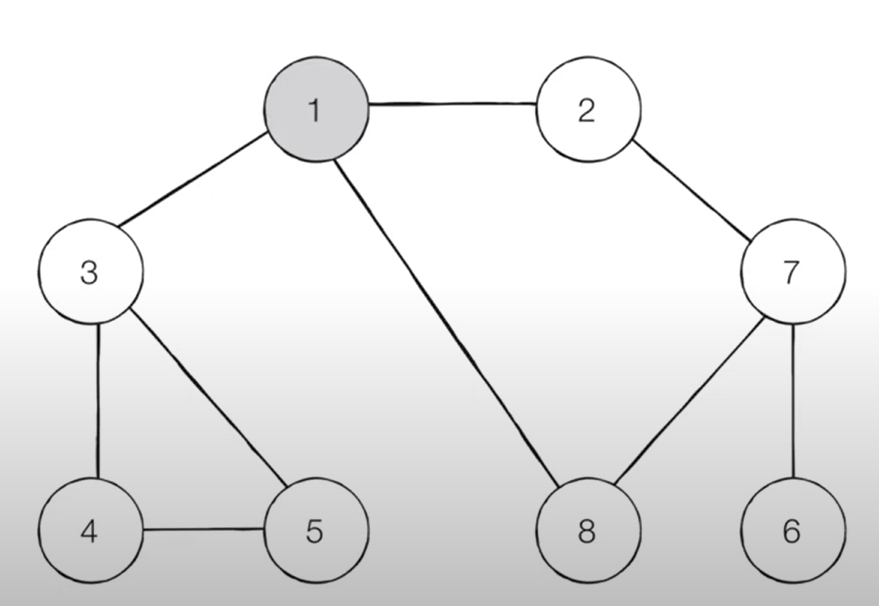
- 풀이
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DFSExample {
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean visited[] = new boolean[9];
public static void dfs(int x) { // 시작 노드
visited[x] = true;
System.out.print(x + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int next = graph.get(x).get(i);
if (!visited[next]) {
dfs(next);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(6).add(7);
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
graph.get(8).add(1);
graph.get(8).add(7);
dfs(1);
}
}
- 출력 결과
1 2 7 6 8 3 4 5
DFS는 스택 자료구조를 이용하며 동작과정을 단계별로 나누면 다음과 같다.
-
탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입
-
시작노드 방문 처리
-
스택의 최상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 노드가 있다 => 인접 노드를 스택에 넣음
방문하지 않은 노드가 없다 => 스택의 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
-
인접 노드로 이동 & 인접 노드 방문 처리 => 3번 과정을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복한다.
점화식의 논리를 이용해 조금 더 요약해서 설명하자면
-
i번째 노드 방문 => i번째 노드 방문 처리
-
i번째 노드의 인접한 노드 중 방문하지 않은 노드 j가 있다 => j번째 노드 push()
방문하지 않은 노드가 없다 => pop()
-
노드 j로 이동 & 노드 j 방문처리 => 1번으로 이동
1~3번을 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복한다.
BFS
DFS의 예제와 같은 그래프로 BFS탐색을 한다.
- 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class ex5_9 {
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
public static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.poll();
System.out.print(x + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(x).size(); i++) {
int y = graph.get(x).get(i);
if (!visited[y]) {
q.offer(y);
visited[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(1).add(3);
graph.get(1).add(8);
graph.get(2).add(1);
graph.get(2).add(7);
graph.get(3).add(1);
graph.get(3).add(4);
graph.get(3).add(5);
graph.get(4).add(3);
graph.get(5).add(3);
graph.get(6).add(7);
graph.get(7).add(2);
graph.get(7).add(6);
graph.get(7).add(8);
graph.get(8).add(1);
graph.get(8).add(7);
bfs(1);
}
}
-
출력결과
1 2 3 8 7 4 5 6
DFS의 동작과정을 단계별로 정리하면 다음과 같다.
- 탐색 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문처리를 한다.
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼내 인접한 노드 중 방문하지 않은 노드를 큐에 삽입한다.
- 2번 과정을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복한다.
마찬가지로 요약하면
- i번째 노드를 큐에 삽입 & 방문처리
- i번째 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 인접한 노드 중 방문하지 않는 노드 j, k, l …을 큐에 삽입한다.
- j, k, l, …에 대해 1번을 수행한다.
1~4 과정을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복
실전문제
- 문제
n * m 크기의 얼음틀이 있다. 구멍이 뚫려 있는 부분은 0, 칸막이가 존재하는 부분은 1 구멍이 뚫려 있는 부분끼리 상, 하, 좌, 우로 붙어있는 경우 서로 연결되어 있는 것으로 간주한다. 이때 얼음 틀의 모양이 주어졌을 때 생성되는 아이스크림의 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오 다음의 4 * 5 얼음 틀 예시에시는 아이스크림이 총 3개 생성된다. //00110 //00011 //11111 //00000
- 풀이
package algorithm;
import java.util.*;
// 1. 이중 반복문으로 돌다가 방문하지 않은 0을 만나면(i, j) 탐색 시작.
// 2. 시작 노드(i, j)를 기준으로 상, 하, 좌, 우 탐색(틀을 벗어나면 무시)
// 3. 인접한 노드가 구멍이 뚫려있는 부분(0)이고 방문하지 않은 부분이라면 인접 노드를 시작노드로 해서 1번과정 반복
public class ex4 {
static int n, m;
static int[][] graph;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int result = 0;
// bfs 동작 단계
// 1. 시작 노드 큐에 offer() & 방문 처리
// 2. 시작 노드 poll() & 인접한 노드 offer() & 방문처리
// 3. 인접 노드를 시작노드로 다시 1번 수행
public static void bfs(int x, int y) {
Queue<Integer> qx = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> qy = new LinkedList<>();
visited[x][y] = true;
qx.offer(x);
qy.offer(y);
while (!qx.isEmpty() && !qy.isEmpty()) {
int currentX = qx.poll();
int currentY = qy.poll();
// (x-1, y), (x+1, y), (x, y-1), (x, y+1)
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tempX = currentX + dx[i];
int tempY = currentY + dy[i];
if (tempX >= 0 && tempX < n
&& tempY >= 0 && tempY < m
&& !visited[tempX][tempY]
&& graph[tempX][tempY] == 0) {
qx.offer(tempX);
qy.offer(tempY);
visited[tempX][tempY] = true;
}
}
}
result++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
graph = new int[n][m];
visited = new boolean[n][m];
// 얼음틀 입력
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 방문하지 않은 0을 만날 때까지 탐색
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] == 0 && visited[i][j] == false) {
bfs(i, j);
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
-
문제
동빈이는 n x m 크기의 직사각형 형태의 미로에 갇혔다. 미로에는 여러 괴물이 있어 피해서 탈출해야함 동빈이의 위치는 (1,1) 미로의 출구는 (n,m) 한번에 한칸씩 이동 가능. 괴물이 있는 부분은 0, 없는 부분 1 동빈이가 탈출하기 위해 움직여야 하는 최소 칸의 개수를 구하시오. 시작칸, 마지막칸 포함해서 계산
입력 5 6 101010 111111 000001 111111 111111
출력 10
package algorithm; import java.util.*; public class ex6 { static int n; static int m; static int[][] graph; static int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0}; static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1}; public static int bfs(int x, int y) { Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(new int[] {x, y}); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int[] current = q.poll(); int currentX = current[0]; int currentY = current[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int nextX = currentX + dx[i]; int nextY = currentY + dy[i]; if (nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < m && graph[nextX][nextY] == 1) { graph[nextX][nextY] = graph[currentX][currentY] + 1; q.offer(new int[] {nextX, nextY}); } } } return graph[n - 1][m - 1]; } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); n = sc.nextInt(); m = sc.nextInt(); sc.nextLine(); graph = new int[n][m]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String str = sc.nextLine(); for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { graph[i][j] = (int)(str.charAt(j) - '0'); } } int result = bfs(0, 0); System.out.println(result); } }
댓글남기기